26 Fun Facts About The Respiratory System
-
The total length of all your airways, unfolded, would stretch a quarter-mile!
-
Millions of smell receptors in your nose help you identify countless odors.
-
Laughter is like exercise for your lungs, increasing oxygen intake.
-
You might not notice, but you breathe mainly through one nostril at a time!
-
We lose about a cup of water every day, just by breathing.
-
Hiccups happen when your diaphragm spasms, causing that hiccough sound.
-
Your lungs hold tiny air sacs called alveoli, with a surface area like a tennis court!
-
Because they’re filled with air, lungs are the only organs that can float on water.
-
Singing can improve lung function and breath control, just like exercise!
-
Your sense of taste is partly linked to sense of smell, which needs good airflow!
-
We take about 20,000 breaths each day, most of them without even realizing it.
-
Dust, pollen can get trapped in the mucus in your nose.
-
Your respiratory system helps regulate your body temperature.
-
The trachea, is Greek word means u0022rough,u0022 which describes the sound of air.
-
Trained detection dogs can use their sense of smell to sniff out explosives!
Table of Contents
1. The right lung is slightly larger than the left lung.
Our lungs are essential for breathing, but did you know they aren’t identical? The right lung is actually bigger than the left lung.
This size difference allows room for the heart, which is situated slightly to the left in our chest. Despite the difference, both lungs work together seamlessly to keep us breathing efficiently.
2. The surface area of the lungs is about the same size as a tennis court.
The human lungs are incredibly efficient organs with a vast surface area. If spread out flat, their surface area would be about the size of a tennis court.
This extensive surface area allows for optimal gas exchange, ensuring that oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide is expelled effectively. It’s truly a remarkable feature of our respiratory system.
3. We breathe in about 13 pints of air every minute.
Breathing is a constant and vital process. On average, a person inhales about 13 pints of air each minute.
This ensures that our bodies receive the necessary oxygen to function properly while also expelling carbon dioxide. It’s amazing how our respiratory system works tirelessly every second of the day.
4. A sneeze can travel up to 100 miles per hour.
READ ALSO: 29 Fun Facts About Nervous System | Electric Facts
Sneezing is a powerful reflex action of the respiratory system. When we sneeze, the expelled air can travel at speeds of up to 100 miles per hour.
This rapid expulsion helps clear irritants from our nasal passages, making it an essential defensive mechanism. It’s a reminder of the respiratory system’s dynamic nature.
5. The lungs are the only organs that can float on water.
Our lungs can float on water! This is due to the air trapped within them.
This buoyancy is unique to the lungs among all our organs, highlighting their distinctive structure and function. It’s a simple yet fascinating aspect of our anatomy.
6. Your nose can remember 50,000 different scents.
Our sense of smell is intricately linked to the respiratory system. The human nose can remember up to 50,000 different scents.
This incredible capability enhances our ability to detect and react to various smells, playing a crucial role in our daily lives. It’s a testament to the complex functions of our respiratory system.
7. The trachea is also known as the windpipe.
The trachea, commonly called the windpipe, is a vital part of the respiratory system. It serves as the main airway to the lungs.
This tube allows air to pass from the nose and mouth into the lungs, facilitating breathing. Understanding its role helps us appreciate the intricacies of our respiratory functions.
8. The diaphragm is the primary muscle used for breathing.

READ ALSO: 30 Fun Facts About Human Body | A Voyage of Learning
Breathing is primarily powered by the diaphragm. This dome-shaped muscle plays a critical role in respiration.
When we inhale, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, creating a vacuum that pulls air into the lungs. It’s a fascinating example of how our body works together to maintain life.
9. The respiratory system also helps regulate body temperature.
Aside from breathing, the respiratory system has other important functions. It helps regulate body temperature.
By adjusting the rate of breathing, the body can control heat loss through the respiratory surfaces, showcasing the system’s multifaceted roles in maintaining homeostasis.
10. We exhale about 17.5 milliliters of water vapor per hour.
Each breath we take is not just about air. We also exhale water vapor, approximately 17.5 milliliters per hour.
This process helps maintain fluid balance in our body, emphasizing the respiratory system’s integral part in overall hydration and health.
11. Hiccups are caused by involuntary contractions of the diaphragm.
Hiccups are a common and sometimes annoying occurrence. They are caused by involuntary contractions of the diaphragm.
These sudden contractions are often triggered by various factors, including eating too quickly or swallowing air. It’s a quirky aspect of our respiratory system.
12. Singing can improve lung function and breathing control.

READ ALSO: 33 Fun Facts About Stomach | Digestive Powerhouse
Singing isn’t just an enjoyable activity; it has health benefits too. Regular singing can enhance lung function and improve breathing control.
It engages the respiratory muscles and promotes better breath management, demonstrating the positive impact of singing on respiratory health.
13. Laughing expands the lungs and increases oxygen intake.
Laughter is indeed the best medicine, especially for the lungs. When we laugh, it expands the lungs and increases oxygen intake.
This natural process boosts our respiratory efficiency and overall well-being. It’s another reason to smile and laugh often!
14. Your sense of taste relies on your respiratory system.
Oxygen plays a crucial role in helping you perceive the flavors of your food. This interdependence showcases the respiratory system’s impact beyond just breathing.
Our ability to taste is partly due to the oxygen in the air, which enhances flavor perception. Without proper respiration, our sense of taste could be dulled.
15. Lung transplant rejection rates are the highest among all transplanted organs.
Lung transplants pose significant challenges due to their high rejection rates. This makes post-transplant care critically important.
Recipients often require rigorous monitoring and immunosuppressive therapy to prevent rejection, highlighting the complexity of lung transplants.
16. Laughing involves a rapid exchange of air, benefiting lung function.

READ ALSO: 22 Fun Facts About Hedgehogs | Spiky Quills
Laughter is more than just a response to humor; it’s also a respiratory activity. It enhances lung function and increases oxygen levels in the bloodstream.
This natural process underscores how beneficial laughing can be for respiratory health, promoting better oxygenation.
17. The trachea, or windpipe, is lined with cartilage rings.
These cartilage rings provide structure and prevent the trachea from collapsing. This is essential for maintaining an open airway during breathing.
The rigidity of these rings ensures that air can flow freely in and out of the lungs, demonstrating the trachea’s vital role.
18. Exercise can increase your breathing rate up to five times.
During intense physical activity, the breathing rate can surge dramatically. This helps supply more oxygen to muscles and remove carbon dioxide efficiently.
Such adaptability of the respiratory system is crucial for meeting the body’s increased oxygen demands during exercise.
19. The lungs contain between 300 and 500 million alveoli.
Alveoli are tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs. Their vast number maximizes the surface area for efficient oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
This extensive network allows for the effective transfer of gases, critical for respiratory efficiency.
20. The diaphragm is the primary muscle used for breathing.
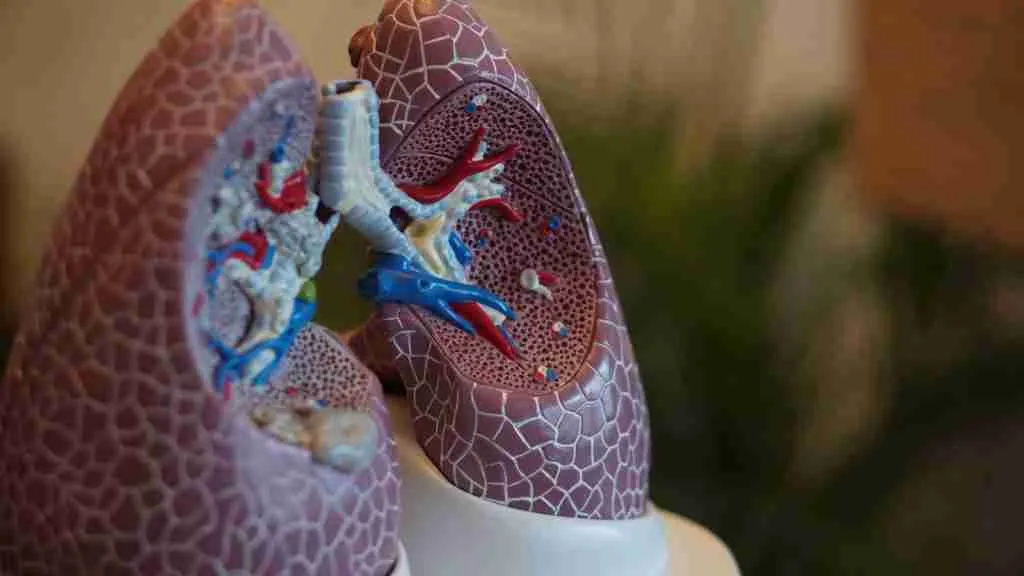
This dome-shaped muscle contracts and flattens during inhalation, creating a vacuum that draws air into the lungs.
Understanding the diaphragm’s function highlights its importance in the breathing process and respiratory health.
21. The body loses approximately 12 ounces of water daily through respiration.
Breathing results in water loss, equivalent to a mini bottle each day. This process is part of maintaining fluid balance in the body.
Especially during physical activity, this water loss can increase, emphasizing the need for hydration.
22. Sneezing can expel air at speeds up to 100 miles per hour.
This powerful reflex helps clear irritants from the nasal passages. Sneezing is an essential defensive mechanism of the respiratory system.
It’s fascinating how such a simple act can be so effective in maintaining respiratory health.
23. Most people breathe through one nostril at a time.
This phenomenon often alternates between nostrils, sometimes changing around sunrise and sunset. It’s part of the body’s natural rhythm.
Understanding this can provide insight into how our respiratory system adapts and functions throughout the day.
24. Breathing helps regulate body temperature.
READ ALSO: 25 Amazing Facts About Teeth You Probably Didn’t Know
Exhaling releases heat, which is especially important during exercise or in hot environments. This thermoregulation is a key function of the respiratory system.
Such regulation helps maintain a stable internal temperature, crucial for overall homeostasis.
25. Some air never leaves the lungs, known as residual volume.
Even after exhaling fully, about 1 to 1.2 liters of air remain in the lungs. This residual volume is essential for preventing lung collapse.
It also helps maintain consistent gas exchange between breaths, ensuring ongoing oxygen supply and carbon dioxide removal.
26. The lungs and windpipe were important symbols in ancient Egypt.
The ancient Egyptians depicted the lungs and windpipe together to symbolize unity and health. This hieroglyph reflected their understanding of respiratory function and its importance.
Such symbolism highlights how ancient cultures revered the respiratory system and its role in sustaining life.
FAQs
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing. It is often managed with inhalers and medications, and by avoiding triggers such as allergens and pollutants. Asthma management aims to control symptoms and prevent asthma attacks.
The digestive system is a group of organs that work together to convert food into energy and basic nutrients to feed the entire body. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The process involves ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination of food and waste.
Common respiratory diseases include asthma, COPD, pneumonia, and bronchitis. Other notable conditions are tuberculosis, pulmonary fibrosis, and lung cancer. These diseases can range from mild to severe and often require medical management.
Diseases that affect the lungs include asthma, COPD, lung cancer, pneumonia, and tuberculosis. Other lung diseases include pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and emphysema. These diseases can significantly impact breathing and overall health.
Common respiratory problems include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchitis, and pneumonia. These conditions can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing. Respiratory problems can be caused by infections, environmental factors, and chronic conditions.